Life expectancy in Sweden is among the highest in the EU, although it declined by nearly one year in 2020 as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic. The healthcare system generally performs well in providing good access to high-quality care.
However, challenges persist in providing equal access to care for the population living in different regions, ensuring timely access to care, achieving greater care coordination for people with chronic diseases and improving the quality of long-term care.
Sweden’s health status
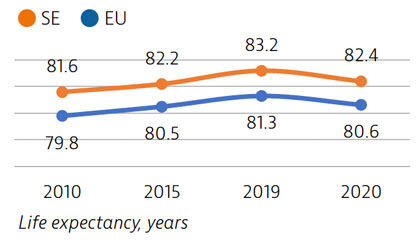
Life expectancy at birth was 82.4 years in 2020 – almost two years above the EU average – but it fell by almost one year in 2020 because of the high number of deaths from Covid-19. More than two thirds of Covid-19 deaths were among people aged 80 and over.
Risk factors
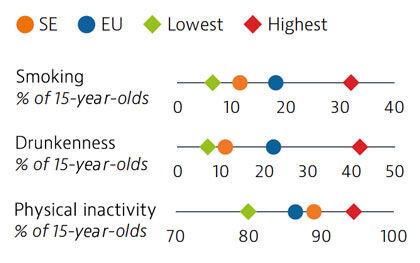
Smoking rates among adults in Sweden are among the lowest in EU countries, but use of other tobacco products such as snuff is common. Overall alcohol consumption per adult has decreased over the past decade and is much lower than the EU average. Adolescents in Sweden also report low rates of smoking and excessive alcohol intake, but high rates of physical inactivity.
Sweden’s health system
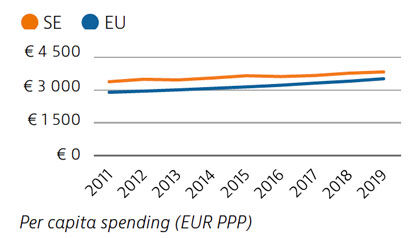
Health spending per capita in Sweden was the fourth highest in the EU in 2019, and the third highest in terms of health spending as a share of GDP. Most health spending is publicly funded (85%). The growth rate in health spending was relatively modest in the years prior to the pandemic, but the government increased spending on health in 2020 and 2021 in response to Covid-19.
Effectiveness
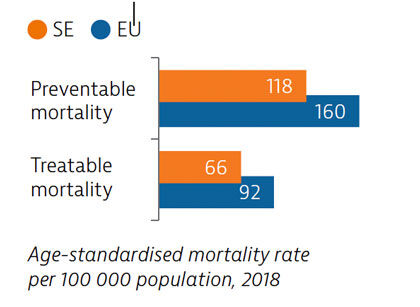
Sweden had low rates of mortality from preventable and treatable causes in 2018, pointing to a generally effective public health and healthcare system under normal circumstances.
Accessibility
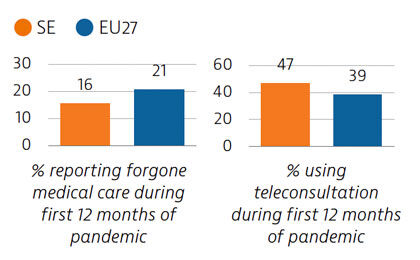
During the first year following the pandemic, one in six people in Sweden reported some unmet needs for medical care, which is slower than the EU average. The use of teleconsultations increased quickly in Sweden during the pandemic to maintain access to care.
Resilience
Sweden tried to balance protection of people’s health and protection of economic and social activities in managing the Covid-19 crisis. While fewer restrictions were imposed, particularly during the first wave, the death toll was high compared with other Nordic countries. By end of August 2021, 58% of the population had received two doses or the equivalent – slightly more than the EU average.
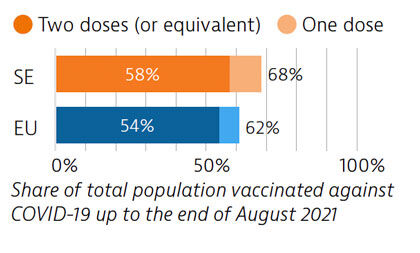
OECD/European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies (2021), Sweden: Country Health Profile 2021, State of Health in the EU, OECD Publishing, Paris/European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies, Brussels.











