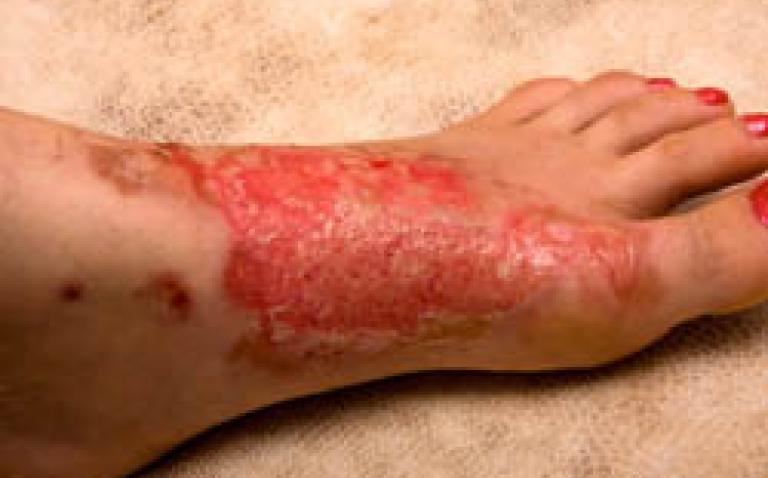
ConvaTec, a world-leading developer and marketer of innovative medical technologies for community and hospital care, today announced the European introduction of the latest products to their most recognised family of wound dressings, AQUACEL™ BURN and the antimicrobial AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressings.
The innovative, new wound dressings are designed to transform the management of partial thickness burns (PTBs) and donor sites. Introduced at the 16th Congress of the International Society for Burn Injuries (ISBI), the dressings incorporate the company’s proprietary Hydrofiber™ Technology, which has been shown in an in vitro study to lock in fluid and trap harmful bacteria[1] and to contour closely to uneven wound surfaces.[2]
It is common practice for patients with PTBs to frequently be subjected to painful dressing changes as often as twice daily, causing severe discomfort and exposing the wound surface to potential infection from a range of deadly pathogens, referred to as ‘superbugs’ that are rampant in many hospitals today.
AQUACEL™ BURN and AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressings, for PTBs, can be left in place for up to 21 days, helping to reduce the need for painful dressing changes and the risk of exposure to deadly pathogens in the atmosphere.[3,4]
In addition to flat dressings, AQUACEL™ BURN and AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressings are available in a one-of-a-kind Hydrofiber™ Technology glove for use specifically in PTBs to hands, where a large number of burn injuries occur. The gloves come in a range of sizes from child to adult.
The dressings are reinforced with Nylon stitching to offer patients the maximum flexibility and range of motion that is essential to ensure that the wound heals properly and prevents contracture, while minimising the risk of infection.
“The design of AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressing is like no other dressing on the market. Working with clinicians, we developed a dressing to help patients improve mobility and flexibility during the period when the burn surface must be covered by a dressing,” said Jorgen Hansen, Senior Vice President, Global Marketing, Business Development and Innovation.
“In vitro studies have shown that our dressings will absorb and hold exudate and deadly bacteria that can prevent healing or increase the risk of infection from the ever-present and increasingly potent superbugs.[5,6] As the burn heals, the dressings self-detach, inflicting less trauma than traditional dressings to the wound and patient.”
The World Health Organization states infections acquired in healthcare settings are the most frequent adverse event in healthcare delivery worldwide.[7]
According to a recent European multicentre study, the proportion of infected patients in intensive care units, where burn patients are often treated, can be as high as 51%.[7] The AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressing incorporates the antimicrobial action of ionic silver, well-proven in vitro to kill a broad spectrum of some of the most resistant pathogens[8], including MRSA, VRE, S. aureus, P.aeruginosa, C. krusei, and B. fragilis.
Using the same antimicrobial activity and Hydrofiber™ Technology as AQUACEL™ Ag dressings, AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressing has been shown to provide activity against antimicrobial resistant bacteria and potentially reduce the risk of infection in vitro.[9]
AQUACEL™ BURN and AQUACEL™ Ag BURN dressings have been tested in clinical studies in both the U.S. and in Europe. In all cases, results showed positive advantages related to patient pain at rest, during movement and ease of use.[10,11]
Advanced Wound Dressings with Hydrofiber Technology from ConvaTec
ConvaTec is the only company to offer wound dressings with Hydrofiber™ Technology that gel on contact with fluid, providing clinicians and patients with substantial wound care benefits.
Used for a wide range of moderate to highly exuding chronic and acute wounds, including surgical, trauma and burn wounds, AQUACEL™ and AQUACEL™ Ag dressings are soft, absorbent, non-woven wound dressings available in a variety of shapes, sizes and formats, including foam.
As demonstrated time and again in a number of in vitro studies, this unique gelling action enables the dressings to lock in exudate and its harmful components[3,12,13] and micro-contour closely to the wound bed,[4] in response to changing wound conditions.
About ConvaTec
ConvaTec is a leading developer and marketer of innovative medical technologies that have helped improve the lives of millions of people worldwide. With four key focus areas – Ostomy Care, Wound Therapeutics, Continence and Critical Care, and Infusion Devices – ConvaTec products support healthcare professionals from the hospital to the community health setting. For more information, please visit www.convatec.com.
References
- Walker M, Hobot JA, Newman GR, Bowler PG. Scanning electron microscopic examination of bacterial immobilisation in a carboxymethyl cellulose (AQUACEL™) and alginate dressing. Biomaterials. 2003;24(5):883-890.
- Jones S, Bowler PG, Walker M. Antimicrobial activity of silver-containing dressings is influenced by dressing conformability with a wound surface. WOUNDS. 2005;17 (9): 263-270.
- Caruso D.M, Foster K.N, Blome-Eberwein S.A, et al. Randomised clinical study of Hydrofiber dressing with silver or silver sulphadiazine in the management of partial-thickness burns. Journal of Burn Care and research. 2006 May/June; 27(3): 298-309
- Walker M, Hobot JA, Newman GR, Bowler PG. Scanning electron microscopic examination of bacterial immobilisation in a carboxymethyl cellulose (AQUACEL™ ™ ) and alginate dressing. Biomaterials. 2003;24(5):883-890.
- Newman GR, Walker M, Hobot JA, Bowler PG. Visualisation of bacterial sequestration and bacterial activity within hydrating Hydrofiber® wound dressings. Biomaterials. 2006;27;1129-1139.
- Bowler PG, Jones SA, Davies BJ, Coyle E. Infection control properties in some wound dressings. J Wound Care 1999;8(10):499-502.
- World Health Organisation. Health care-associated infections Fact Sheet. http://www.who.int/gpsc/country_work/gpsc_ccisc_fact_sheet_en.pdf. Accessed August 23, 2012.
- Jones SA, Bowler PG, Walker M, Parsons D. Controlling wound bioburden with a novel silver-containing Hydrofiber dressing. Wound Repair Regen. 2004;12(3):288-294.
- The microbicidal properties of Apollo burn dressing. WHRI3239 MA 132. May 2009. Data on file, ConvaTec Inc.
- Caruso DM,1 Richey K,1 Johnson RM,2 Blome-Eberwein SA,3 Milner S,4 Luterman A,5 Tredget EE,6 Kommala D7. (2009). Phase II, Non-Comparative Trial of Carboxymethylcellulose Silver Dressing Reinforced With Nylon to Treat Partial Thickness Burns.
- Franck Duteille, MD1; Dheerendra Kommala, MD2. (2010, March). Phase II Assessment of a New Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) Silver Glove in the Management of Partial-Thickness/Second-Degree Hand Burn. Poster session presented at the 42nd Annual Meeting of the American Burn Association.
- Waring MJ, Parsons D. Physico-chemical characterization of carboxymethylated spun cellulose fibres. Biomaterials. 2001;22:903-912.
- Walker M, Bowler PG, Cochrane CA. In vitro studies to show sequestration of matrix metalloproteinases by silver-containing wound care products. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2007;53(9):18-25.